General Information
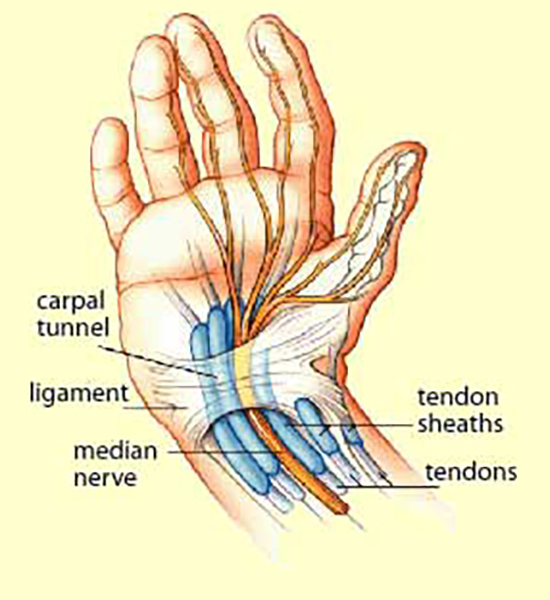
The carpal tunnel is the area under a ligament (a tough, elastic band of tissue that connects bones and organs in place) in front of the wrist. The median nerve, which passes through the carpal tunnel, supplies the thumb side of the hand.
Repetitive movements of the hand and wrist can cause inflammation of structures (such as tendons and their coverings) that surround the median nerve. The inflammation may compress this nerve, producing numbness, tingling, and pain in the first three fingers and the thumb side of the hand-a condition known as carpal tunnel syndrome.

Signs & Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
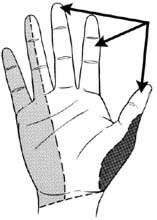 Carpal tunnel syndrome is compression or pressure on the median nerve at the wrist level. Alignment at the wrist creates a tunnel through which the median nerve and nine tendons course. The median nerve supplies sensation to the thumb, index, long finger and half of the ring finger, thus patients’ complaints are altered sensation in these digits. You can test yourself for carpal tunnel syndrome by simply maximally bending the wrist down and waiting one minute. If you have increased symptoms of abnormal feeling in these digits, then you may well have carpal tunnel syndrome.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is compression or pressure on the median nerve at the wrist level. Alignment at the wrist creates a tunnel through which the median nerve and nine tendons course. The median nerve supplies sensation to the thumb, index, long finger and half of the ring finger, thus patients’ complaints are altered sensation in these digits. You can test yourself for carpal tunnel syndrome by simply maximally bending the wrist down and waiting one minute. If you have increased symptoms of abnormal feeling in these digits, then you may well have carpal tunnel syndrome.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
There can be many causes of carpal tunnel syndrome. Jobs that require excessive bending of the wrist tend to increase the pressure around the median nerve in the wrist. Similarly, sleeping with your wrist in an acutely bent position will increase pressure on the median nerve and cause carpal tunnel syndrome. Diabetes, alcoholism, hypothyroidism and obesity are also all factors towards developing carpal tunnel syndrome.
Treatments for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome can vary from just a small amount of pressure to extreme pressure, and in the late stages of carpal tunnel syndrome, surgery may be necessary to release a short ligament at the wrist level. Earlier on, the best treatment will involve using a splint which keeps your wrist completely flat and is worn at night. This will decrease the excessive pressure that can develop at night when the wrist naturally goes into a bent position. Make sure that the splint you wear at night keeps your wrist completely flat.
Faq’s About Carpal Tunnel Surgery
What about Laser Carpal Tunnel Surgery?
There have been no published reports to suggest that laser can improve or cure carpal tunnel syndrome.
What About Endoscopic Carpal Tunnel Surgery?
The “classic” surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome involves an open technique where a small incision is made over the region of the ligament that compresses the median nerve. This ligament is released to decompress the median nerve. With the introduction of endoscopic surgery in other locations in the body, some hand surgeons are using a similar technique at the wrist. Usually two small incisions would be substituted for one larger incision at the wrist level. The incidence of nerve, tendon or blood vessel injury is slightly higher with the endoscopic surgery. Because of the increased risk associated with endoscopic carpal tunnel surgery, the majority of surgeons (including Dr. Concannon) prefer an open technique. It is recommended that you discuss in detail these two types of surgery with the particular surgeon you have chosen to do your surgery.
I Know several people who have had carpal tunnel surgery and It has not improved their symptoms. Why would this be?
The likely answer is that these people have other things going on rather than just carpal tunnel syndrome. Remember that carpal tunnel syndrome will only produce altered sensation in the thumb, index, long and half of the ring finger. Any other symptoms that you have of pain or numbness in the upper extremity may not be due to carpal tunnel syndrome, and should be evaluated for other levels of nerve compression or muscle and tendon problems.
I know one person who following their carpal tunnel surgery had worse pain with a burning sensation at the incision and numbness and pain in the ring and long fingers. What should they do?
This may relate to a small nerve injury of the median nerve. If is does not resolve over a few months, they should seek a surgical consultation as this is not the “normal” course following carpal tunnel surgery.
